About
The Vogon Browser is a revolutionary platform that seamlessly integrates with the Vogon Distributed Quantum Ledger Database (DQLDB) to provide a decentralized, secure, and quantum-resilient browsing experience. It leverages cutting-edge technologies, including Base58 address communication, post-quantum cryptography with SPHINCS+, and DQLDB integration for WEB 5 content access.
With features like VogonID authentication, GICS-based bookmarks, and compliance with KYC, KYB, and AML standards, the browser ensures secure user interactions, encrypted data transmission, and immutable content publishing. Designed for future-proof internet interaction, it bridges current web functionality with the decentralized web's possibilities.
1. Secure Access with VogonID
VogonID Authentication
Mandatory VogonID
Users must possess a VogonID to access the browser, ensuring a secure and authenticated user base.
Enhanced Security
VogonID utilizes post-quantum cryptographic methods like SPHINCS+ to protect user identities.
Compliance with KYC, KYB, and AML
Regulatory Compliance
Users undergo KYC, KYB, and AML checks before being granted a VogonID.
Secure Posting
Only verified users can post data on Vogon, reducing fraud and malicious activities.
2. B58 Address to Address Communication
Direct Interactions
The browser supports Base58 (B58) encoded addresses, allowing users to interact directly without intermediaries.
Secure Transactions
B58 addresses enhance security and simplify the process of sending and receiving data across the network.
3. DQLDB - WEB 5 Viewing
Next-Generation Web
The browser provides access to WEB 5 content stored on the Vogon DQLDB, pushing beyond traditional web capabilities.
Decentralized Content
Users can view and interact with decentralized applications and services directly through the browser.
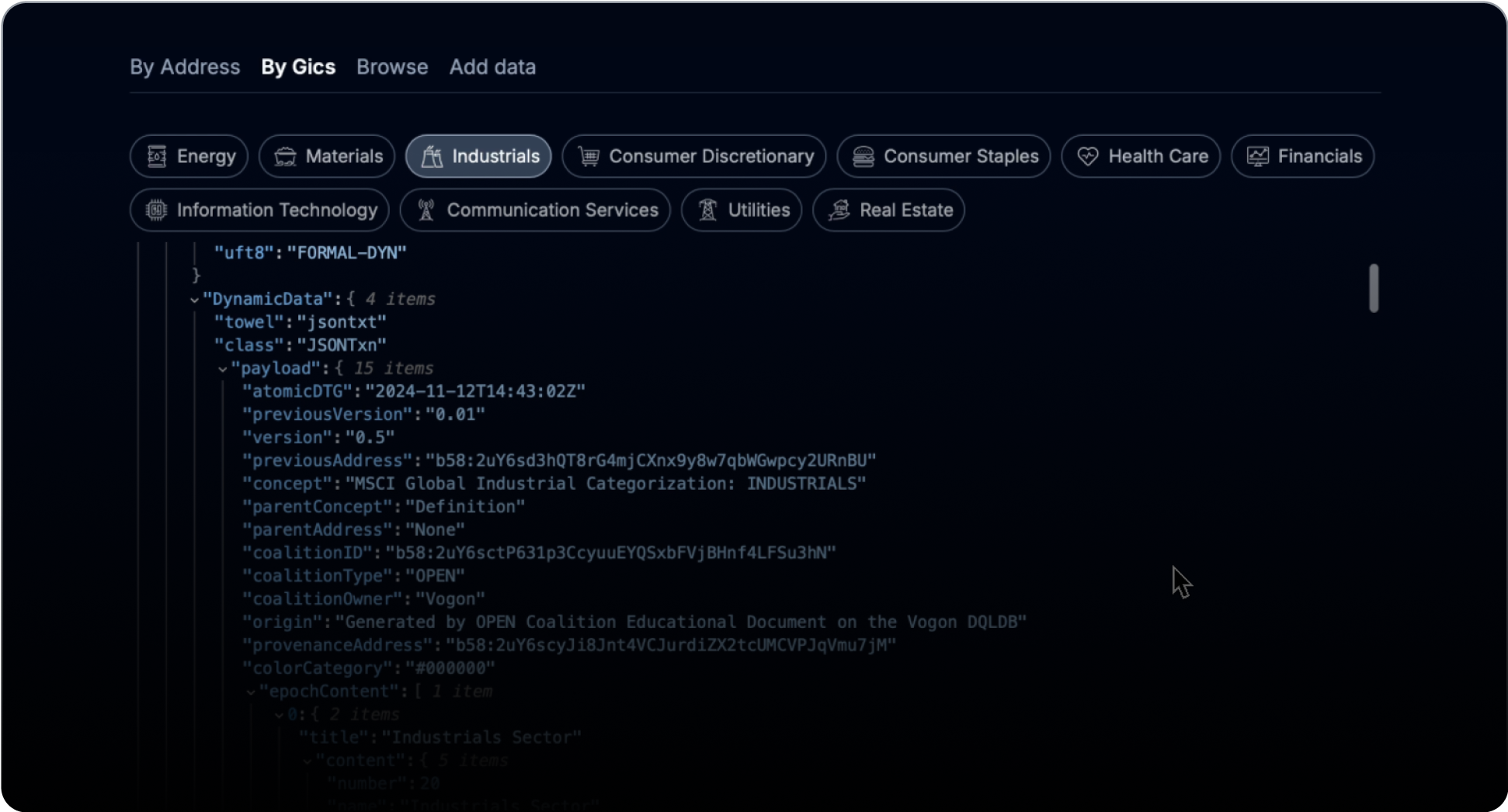
4. GICS Bookmarks
Global Industry Classification Standard (GICS)
Organize bookmarks using GICS, allowing for efficient categorization and retrieval.
Personalized Experience
Enhance user experience by providing structured and industry-standard bookmarking.
5. Browsing and Posting Data
Secure Browsing
Encrypted Data Transmission
All browsing activities are encrypted using quantum-resistant algorithms.
Privacy Protection
User data is protected, ensuring privacy and data integrity.
Posting Data on Vogon
Verified Contributions
Only KYC/KYB and AML-verified users can post data, enhancing the quality and trustworthiness of content.
Decentralized Publishing
Users can publish content directly to the DQLDB, enabling immutable and censorship-resistant information sharing.
6. Real-Time Quantum Interactions
Visualizing Quantum States
Explores visualizing quantum states like superposition and entanglement through interactive tools.
Dynamic Data Updates
The browser integrates real-time updates from DQLDB, ensuring that users always have access to the latest immutable records.
Human Identity Verification
Utilizes advanced biometric and behavioral data to verify and manage identities securely on the quantum ledger.
Utility of Worth Calculation
Describes the process of calculating the utility of worth for Quantum Digital Assets (QDAs) using real-time data and quantum algorithms.
Quansification
Quansification is the process of encoding the intrinsic, contextual, and multidimensional value of an asset into a quantized state within a quantum-ready framework. It ensures that the asset is structured, secured, and enriched using quantum principles and advanced cryptographic methods, making it resilient, adaptive, and interoperable in the quantum ecosystem. Quansification is the culmination and validation of the Quantum Utility of Worth Workflow (QUW). As each step in the QUW Workflow is executed, the asset progresses toward becoming a Quantum Digital Asset (QDA).
Decentralized Identity Management
Discusses the implementation of decentralized identifiers (DIDs) that allow users to control their identity information without relying on central authorities.
Quantum-Enhanced Security Protocols
Details the security protocols enhanced by quantum technologies, ensuring robust protection against evolving cyber threats.
Governance Framework
Outlines the governance structures and policies that regulate the operation and use of the DQLDB, ensuring fair and transparent management of quantum digital assets.
Data Lineage and Traceability
Explains the mechanisms for tracking the history and transformations of data within the DQLDB, ensuring accountability and transparency in data handling.
Asset Provenance Verification
Details the processes involved in verifying the origin and history of quantum digital assets, crucial for establishing trust and authenticity.
Pedigree Management
Discusses the role of pedigree management in documenting and certifying the lineage and transformations of assets, ensuring that ownership and origin are clearly defined and preserved.
7. Educational Tools for Quantum Technologies
Interactive Tutorials
Interactive Tutorials
Built-in tutorials guide users through quantum concepts like DQLDB, SPHINCS+, and Base58 address interactions.
Glossary Integration
The browser includes an embedded glossary and contextual tips to simplify complex terminology for all users.
8. Personalized Quantum-Aware Browsing
Adaptive Recommendations
Adaptive Recommendations
Quantum-enhanced algorithms analyze user preferences to offer personalized content suggestions.
Customizable GICS Bookmarks
Users can categorize and organize bookmarks dynamically based on browsing habits and industry trends.
9. Seamless Integration of Classical and Quantum Systems
Dual Compatibility
The browser supports both traditional Web 2.0/3.0 and decentralized Web 5 systems, enabling a smooth transition for users.
Comprehensive Data Navigation
The epoch footer serves as a centralized navigational hub, seamlessly connecting Distributed Quantum Ledger Database (DQLDB) entries to traditional Web 2.0 and decentralized Web 5 environments. With B58 decentralized identifiers and HTTPS links, users can traverse datasets, sectors, and external systems efficiently and intuitively.
Integrated Quantum Guidance
The epoch footer embeds mathematical expressions that act as directives for quantum chips, enabling dynamic processing and optimization of data. This ensures that quantum computations align with contextual metadata, facilitating advanced problem-solving and adaptive quantum-state transitions.
Unified Web and Quantum Ecosystem
By incorporating navigation links for both quantum data and traditional web systems, the epoch footer bridges the gap between classical and quantum technologies. It supports interoperability across Web 5 decentralized identifiers and Web 2.0 standards, creating a cohesive ecosystem for hybrid applications.
Interoperable Data Formats
Native support for classical formats alongside quantum-enabled structures like Base58 addresses ensures versatility.
10. Expanded Security Details
Post-Quantum Encryption
Post-Quantum Encryption
The SPHINCS+ algorithm protects against quantum computing attacks, ensuring long-term data security.
Immutable Ledger Records
Every transaction is recorded on the DQLDB with full traceability and tamper-proof guarantees.
Conclusion
The Vogon Browser revolutionizes the way users interact with the web by integrating advanced security measures, decentralized technologies, and compliance standards. By requiring VogonID authentication and adhering to KYC/KYB and AML regulations, it ensures a secure environment for browsing and data posting. Features like B58 Address communication, DQLDB - WEB 5 viewing, and GICS bookmarks provide users with a next-generation browsing experience, bridging the gap between current internet technologies and the future of decentralized web services.
